CFD-FVM-12: Implementation of boundary conditions

Introduction
The most common boundary conditions:
- inlet
- outlet
- wall
- prescribed pressure
- symmetry
- periodicity (or cyclic boundary condition)
Note that additional nodes outside the boundary are required to store values that correlate with the boundary conditions, as shown in the figure below:
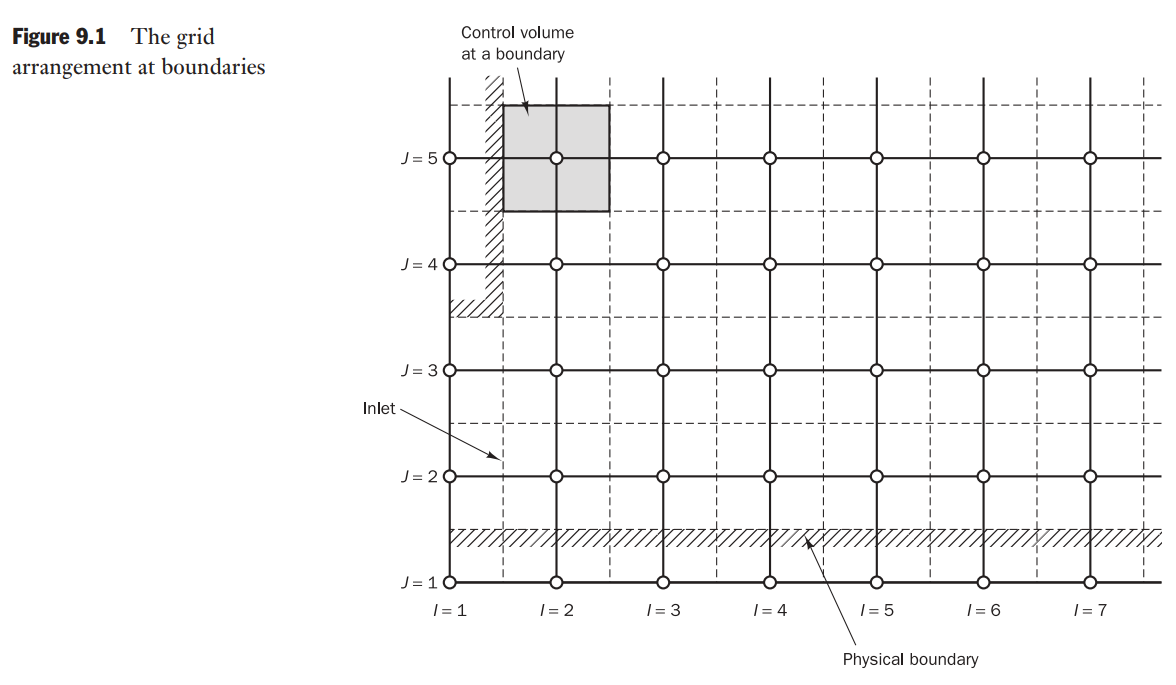
In this chapter, we make the following assumptions:
- the flow is always subsonic (M < 1),
turbulence modelling is used, - the hybrid differencing method is used for discretisation and
- the SIMPLE solution algorithm is applied
Inlet boundary conditions
Figures 9.2 to 9.5 show the grid arrangement in the immediate vicinity of an inlet for
The figures indicate that all links to neighbouring nodes remain active for the first
Figure 9.4 shows that the link with the boundary side is cut in the discretised pressure correction equation by setting the boundary side (west) coefficient




Outlet boundary conditions
If the location of the outlet is selected far away from geometrical disturbances the flow eventually reaches a fully developed state where no change occurs in the flow direction. In such a region we can place an outlet surface and state that the gradients of all variables (except pressure) are zero in the flow direction.




Before the relevant equations are solved the values of flow variables at the next node (NI), just outside the domain, are determined by extrapolation from the interior on the assumption of zero gradient at the outlet plane.
To make the mass flux out equal to the mass flux
Wall boundary conditions



See original book for how to deal with Laminar flow / linear sub-layer and Turbulent flow near wall.
The constant pressure boundary condition
Typical problems where this boundary condition is appropriate include external flows around objects, free surface flows, buoyancy-driven flows such as natural ventilation and fires, and also internal flows with multiple outlets.


A convenient way of dealing with a constant pressure boundary condition is to fix pressure at the nodes just inside the physical boundary, as indicated in the diagrams by solid squares.
Symmetry boundary condition
The conditions at a symmetry boundary are:
- no flow across the boundary
- no scalar flux across the boundary.
Periodic or cyclic boundary condition
Easy to understand, see original book for details.